Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (HMB) is a condition that affects many women globally. It is characterised by abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, which can significantly disrupt daily life. Dr. Saurabh Phadnis in London offers trusted, professional care to help women understand, manage, and treat this condition effectively. If you’re experiencing symptoms of HMB, it’s important to understand its causes, available treatments, and potential relief options.
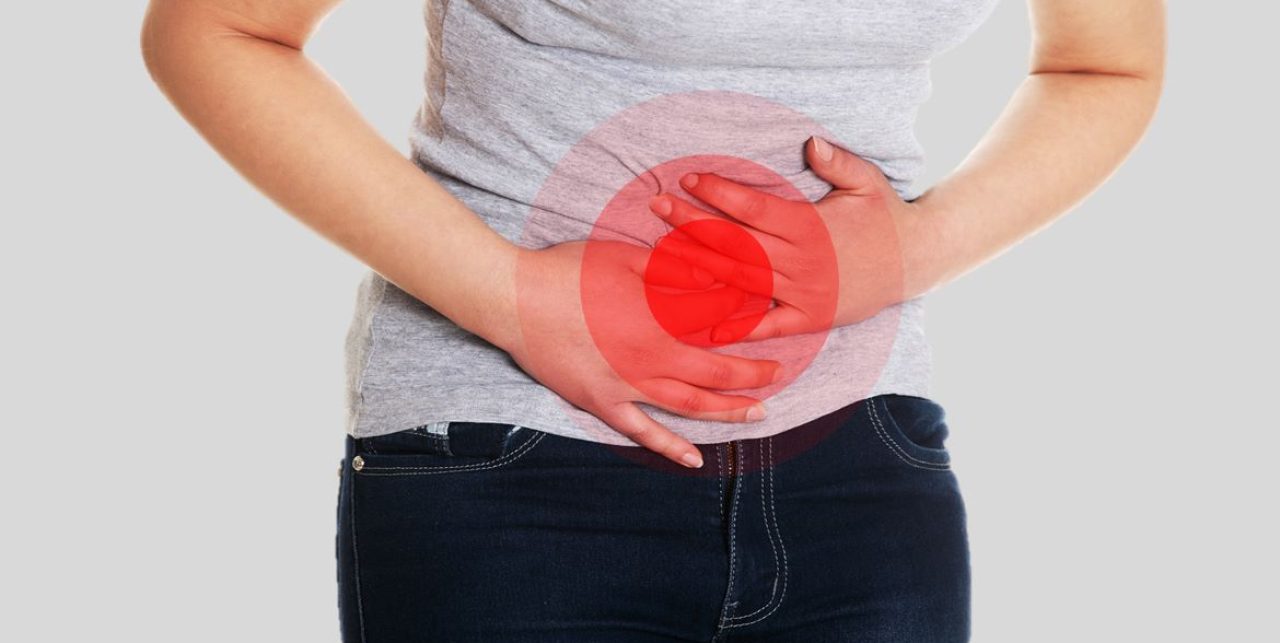

Heavy Menstrual Bleeding, also known as menorrhagia, refers to excessively heavy or prolonged menstrual periods. While a typical menstrual cycle lasts between 3 to 7 days, women suffering from HMB may experience bleeding that lasts longer than 7 days, or the flow may be much heavier than normal.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding can occur due to various underlying causes. In some cases, hormonal imbalances or structural issues in the uterus may be the reason for heavy bleeding.


Below are some of the common causes:
The menstrual cycle is regulated by hormones, mainly estrogen and progesterone. A hormonal imbalance, particularly an excess of estrogen, can cause the uterine lining to thicken, leading to heavier bleeding.
Uterine fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) growths that develop within the uterine walls. These fibroids can lead to excessive bleeding due to their size and location.
This condition occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows into the muscle walls of the uterus. This can cause heavier than normal periods and can also lead to pain during menstruation.
Endometrial polyps are small growths attached to the inner wall of the uterus, often caused by hormonal imbalances.
Conditions like thyroid disorders, blood clotting disorders (e.g., von Willebrand disease), and certain cancers (such as uterine or cervical cancer) can lead to HMB.
Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can increase the likelihood of heavy bleeding.
While some degree of menstrual variation is normal, persistent heavy bleeding may indicate the presence of HMB.


Dr. Saurabh Phadnis in London, will typically use a variety of diagnostic methods to understand the cause and severity of the condition.
The treatment choice will depend on the severity of the condition, underlying causes, and the patient’s overall health.

If you’re experiencing symptoms of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding, Dr. Saurabh Phadnis offers expert care in London to help diagnose, manage, and treat the condition effectively.
Whether you need advice on treatment options, or you’re seeking relief from heavy periods, you can count on professional and compassionate care to improve your quality of life.

If you’re concerned about Heavy Menstrual Bleeding, private consultations are available with Dr. Saurabh Phadnis, leading Gynaecologist, Oncologist, Surgeon, and Co-Lead Colposcopist based in London; specialising in gynaecological cancer. You can visit his clinic or call directly to book an appointment and receive expert care, advice, and personalised treatment.
The most common causes are hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, and polyps. These conditions can cause the uterine lining to shed excessively during menstruation.
If you are soaking through one or more pads or tampons every hour, or if your period lasts longer than 7 days, it may indicate heavy menstrual bleeding.
Yes, many women find relief from Heavy Menstrual Bleeding through hormonal therapy, non-hormonal medications, and lifestyle changes without needing surgery.
While not all causes are preventable, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, exercising regularly, and having regular medical check-ups can help reduce the risk.
In some cases, it can be a symptom of underlying issues like fibroids, adenomyosis, or even cancer. It’s important to seek medical attention if heavy bleeding persists.
Specialising in the field of gynaecological cancer, covering the entire spectrum from diagnosis to treatment and post-treatment care.